Tensor Sensor
See article Clarifying exceptions and visualizing tensor operations in deep learning code.
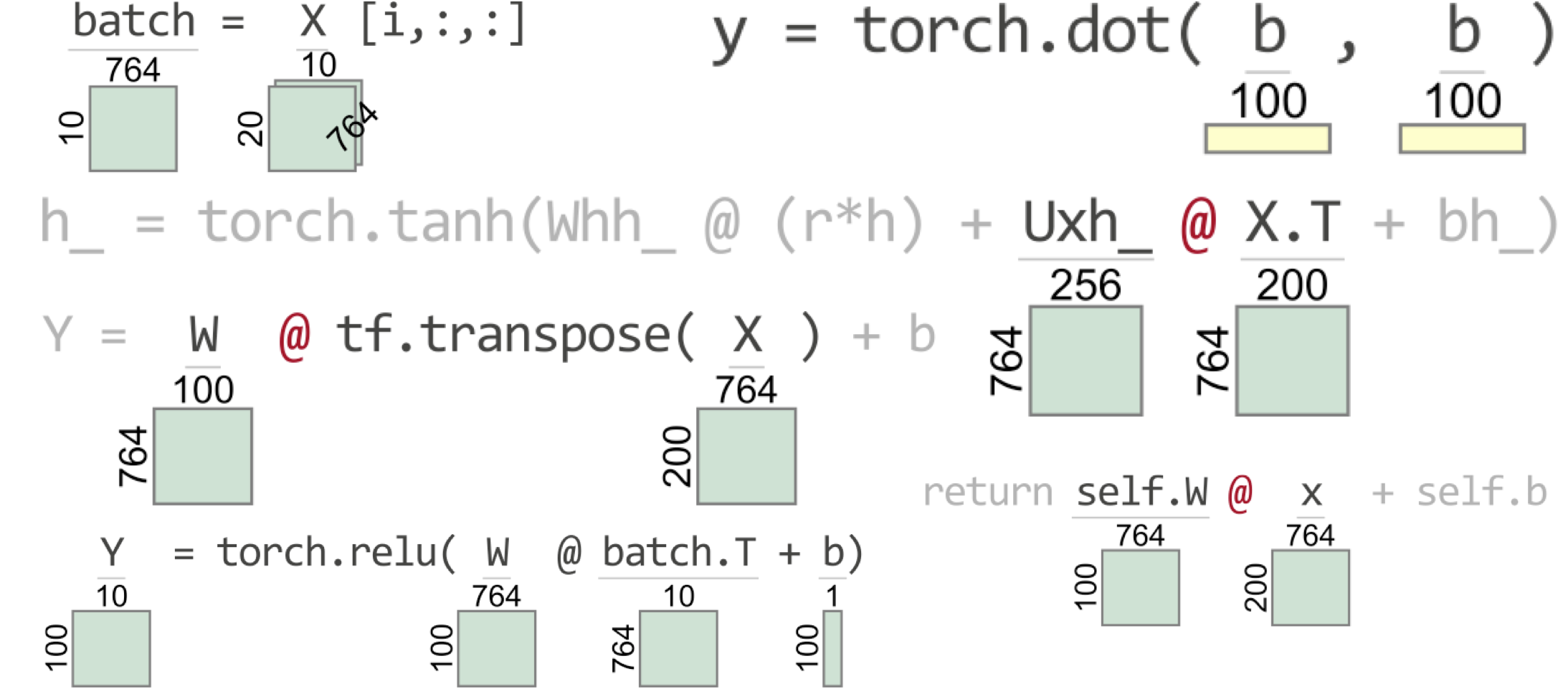
To help myself and other programmers debug tensor code, I built this library. TensorSensor clarifies exceptions by augmenting messages and visualizing Python code to indicate the shape of tensor variables (see figure to the right for a teaser). It works with Tensorflow, PyTorch, JAX, and Numpy, as well as higher-level libraries like Keras and fastai.
TensorSensor is currently at 0.1 (Dec 2020) so I'm happy to receive issues created at this repo or direct email.
Visualizations
For more, see examples.ipynb.
import torch
W = torch.rand(d,n_neurons)
b = torch.rand(n_neurons,1)
X = torch.rand(n,d)
with tsensor.clarify():
Y = W @ X.T + b
Displays this in a jupyter notebook or separate window:
Instead of the following default exception message:
RuntimeError: size mismatch, m1: [764 x 100], m2: [764 x 200] at /tmp/pip-req-build-as628lz5/aten/src/TH/generic/THTensorMath.cpp:41
TensorSensor augments the message with more information about which operator caused the problem and includes the shape of the operands:
Cause: @ on tensor operand W w/shape [764, 100] and operand X.T w/shape [764, 200]
You can also get the full computation graph for an expression that includes all of these sub result shapes.
tsensor.astviz("b = W@b + (h+3).dot(h) + torch.abs(torch.tensor(34))", sys._getframe())
yields the following abstract syntax tree with shapes:
Install
pip install tensor-sensor # This will only install the library for you
pip install tensor-sensor[torch] # install pytorch related dependency
pip install tensor-sensor[tensorflow] # install tensorflow related dependency
pip install tensor-sensor[jax] # install jax, jaxlib
pip install tensor-sensor[all] # install tensorflow, pytorch, jax
which gives you module tsensor. I developed and tested with the following versions
$ pip list | grep -i flow
tensorflow 2.3.0
tensorflow-estimator 2.3.0
$ pip list | grep -i numpy
numpy 1.18.5
numpydoc 1.1.0
$ pip list | grep -i torch
torch 1.6.0
$ pip list | grep -i jax
jax 0.2.6
jaxlib 0.1.57
Graphviz for tsensor.astviz()
For displaying abstract syntax trees (ASTs) with tsensor.astviz(...), then you need the dot executable from graphviz, not just the python library.
On Mac, do this before or after tensor-sensor install:
brew install graphviz
On Windows, apparently you need
conda install python-graphviz # Do this first; get's dot executable and py lib
pip install tensor-sensor # Or one of the other installs
Limitations
I rely on parsing lines that are assignments or expressions only so the clarify and explain routines do not handle methods expressed like:
def bar(): b + x * 3
Instead, use
def bar():
b + x * 3
watch out for side effects! I don't do assignments, but any functions you call with side effects will be done while I reevaluate statements.
Can't handle \ continuations.
With Python threading package, don't use multiple threads calling clarify(). multiprocessing package should be fine.
Also note: I've built my own parser to handle just the assignments / expressions tsensor can handle.
Deploy (parrt's use)
$ python setup.py sdist upload
Or download and install locally
$ cd ~/github/tensor-sensor
$ pip install .
TODO
- can i call pyviz in debugger?









