mkdocstrings
Automatic documentation from sources, for MkDocs.
Features
- Language agnostic: just like
mkdocs,mkdocstringsis written in Python but is language-agnostic. It means you can use it for any language, as long as you implement ahandlerfor it. Currently, we only have a Python handler. Maybe you'd like to contribute another one😉 ? - Multiple themes support: each handler can offer multiple themes. Currently, we offer the
⭐ Material theme⭐ as well as basic support for the ReadTheDocs theme for the Python handler. - Cross-references to other objects:
mkdocstringsmakes it possible to reference other headings from your Markdown files with the classic Markdown syntax:[identifier][]or[title][identifier]. This feature is language agnostic as well: you can cross-reference any heading that appear in your Markdown pages. If the handler for a particular language renders headings for documented objects, you'll be able to reference them! - Inline injection in Markdown: instead of generating Markdown files,
mkdocstringsallows you to inject documentation anywhere in your Markdown contents. The syntax is simple:::: identifierfollowed by a 4-spaces indented YAML block. The identifier and YAML configuration will be passed to the appropriate handler to collect and render documentation. - Global and local configuration: each handler can be configured globally in
mkdocs.yml, and locally for each "autodoc" instruction. - Watch source code directories: you can tell
mkdocstringsto add directories to be watched bymkdocswhen serving the documentation, for auto-reload. - Sane defaults: you should be able to just drop the plugin in your configuration and enjoy your auto-generated docs.
Python handler features
- Data collection from source code: collection of the object-tree and the docstrings is done by
pytkdocs. The following features are possible thanks to it:- Support for type annotations:
pytkdocscollects your type annotations andmkdocstringsuses them to display parameters types or return types. - Recursive documentation of Python objects: just use the module dotted-path as identifier, and you get the full module docs. You don't need to inject documentation for each class, function, etc.
- Support for documented attribute: attributes (variables) followed by a docstring (triple-quoted string) will be recognized by
pytkdocsin modules, classes and even in__init__methods. - Support for objects properties:
pytkdocsdetects if a method is astaticmethod, aclassmethod, etc., it also detects if a property is read-only or writable, and more! These properties will be displayed next to the object signature bymkdocstrings. - Google-style sections support in docstrings:
pytkdocsunderstandsArguments:,Raises:andReturns:sections, and returns structured data formkdocstringsto render them. - reStructuredText-style sections support in docstrings:
pytkdocsunderstands all the reStructuredText fields, and returns structured data formkdocstringsto render them. Note: only RST style is supported, not the whole markup. - Admonition support in docstrings: blocks like
Note:orWarning:will be transformed to their admonition equivalent. We do not support nested admonitions in docstrings! - Support for reStructuredText in docstrings:
pytkdocscan parse simple RST.
- Support for type annotations:
- Every object has a TOC entry: we render a heading for each object, meaning
mkdocspicks them into the Table of Contents, which is nicely display by the Material theme. Thanks tomkdocstringscross-reference ability, you can even reference other objects within your docstrings, with the classic Markdown syntax:[this object][package.module.object]or directly with[package.module.object][] - Source code display:
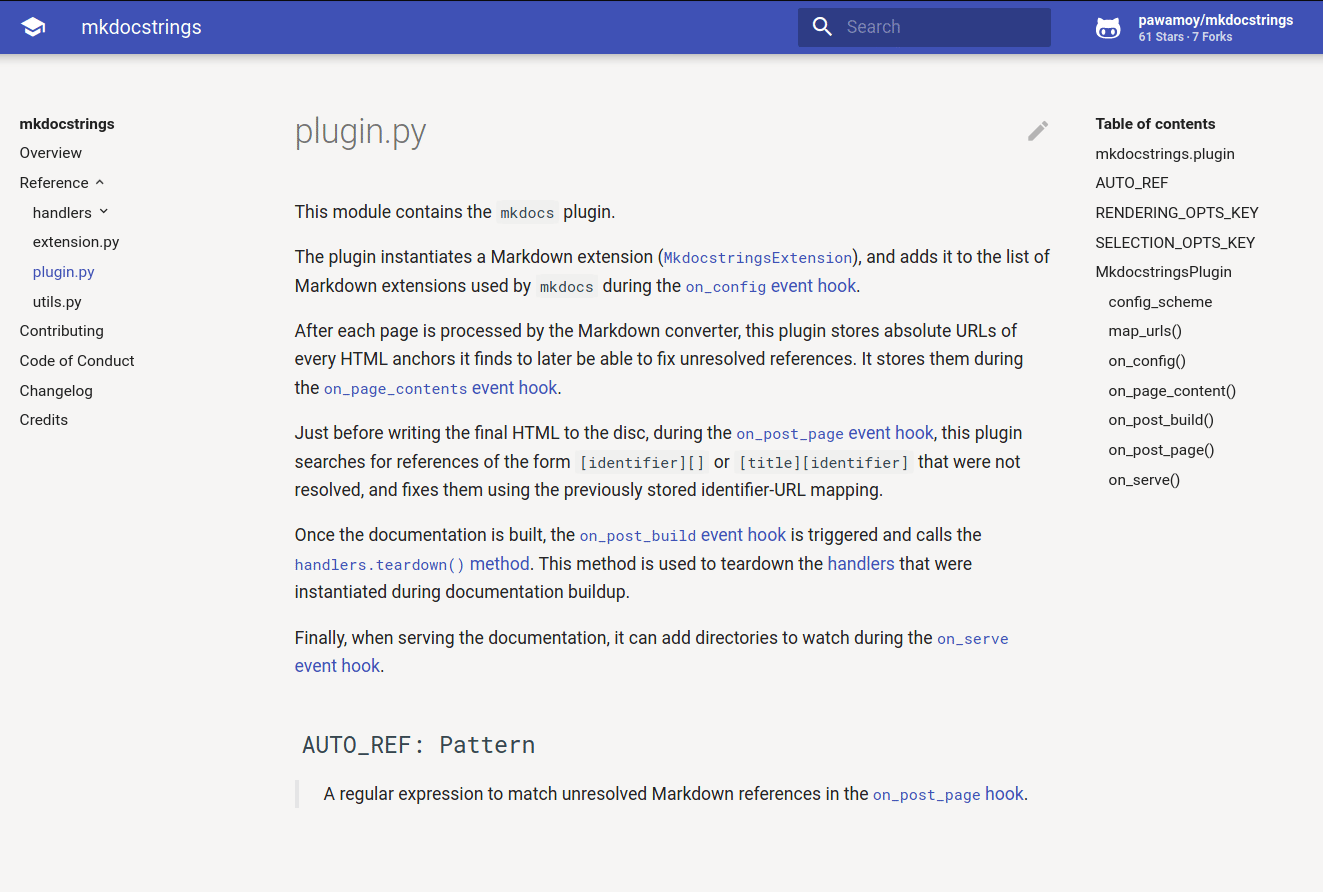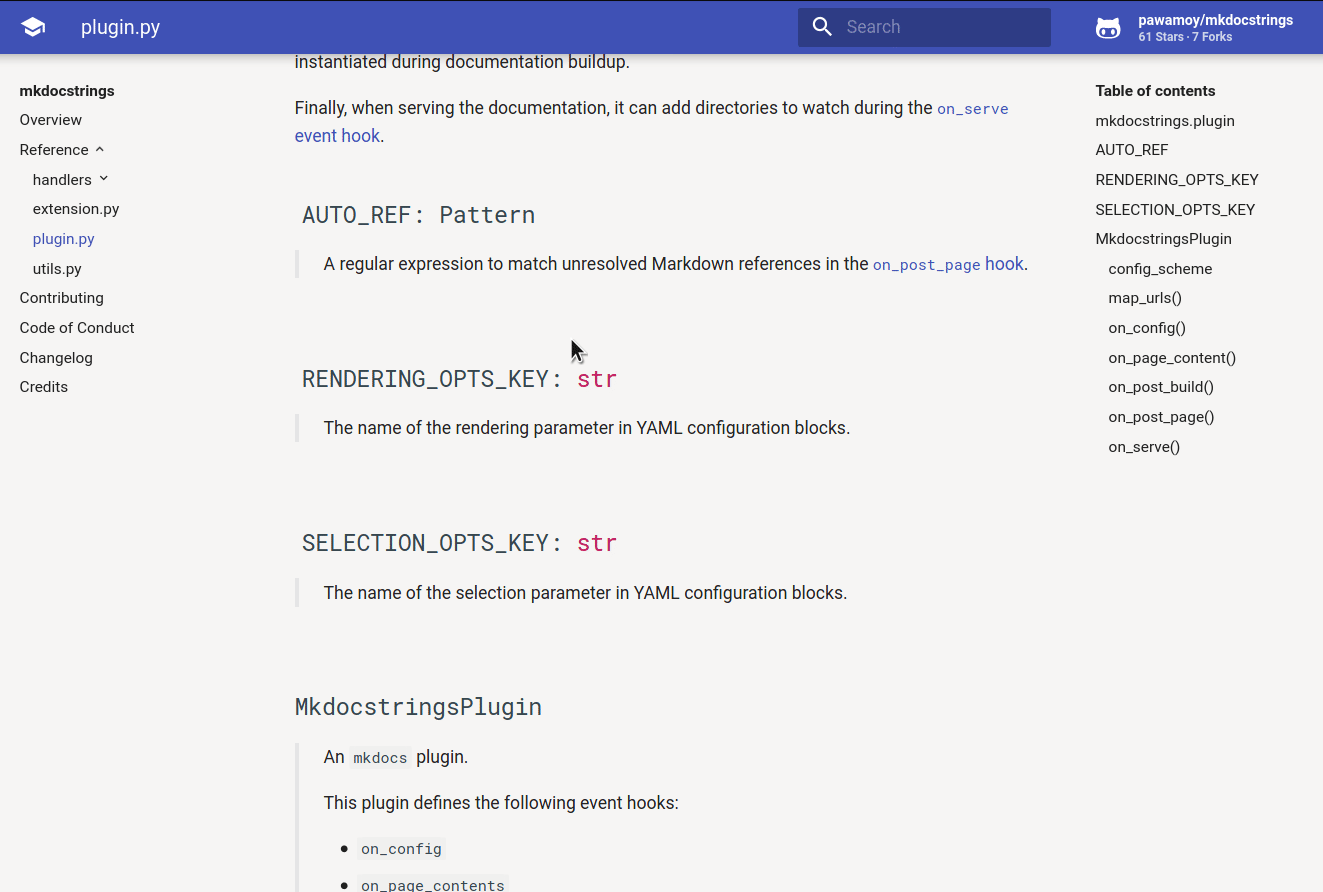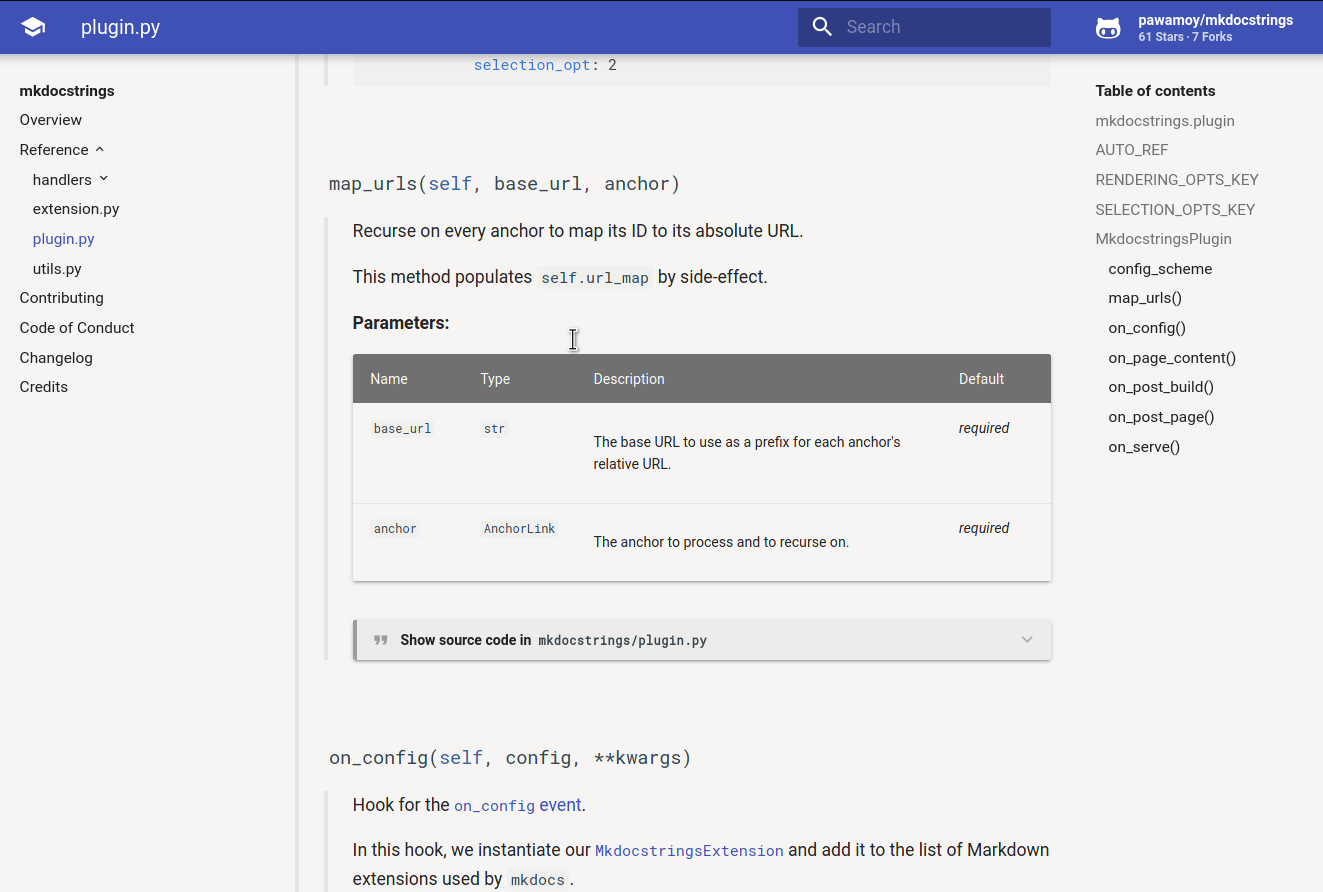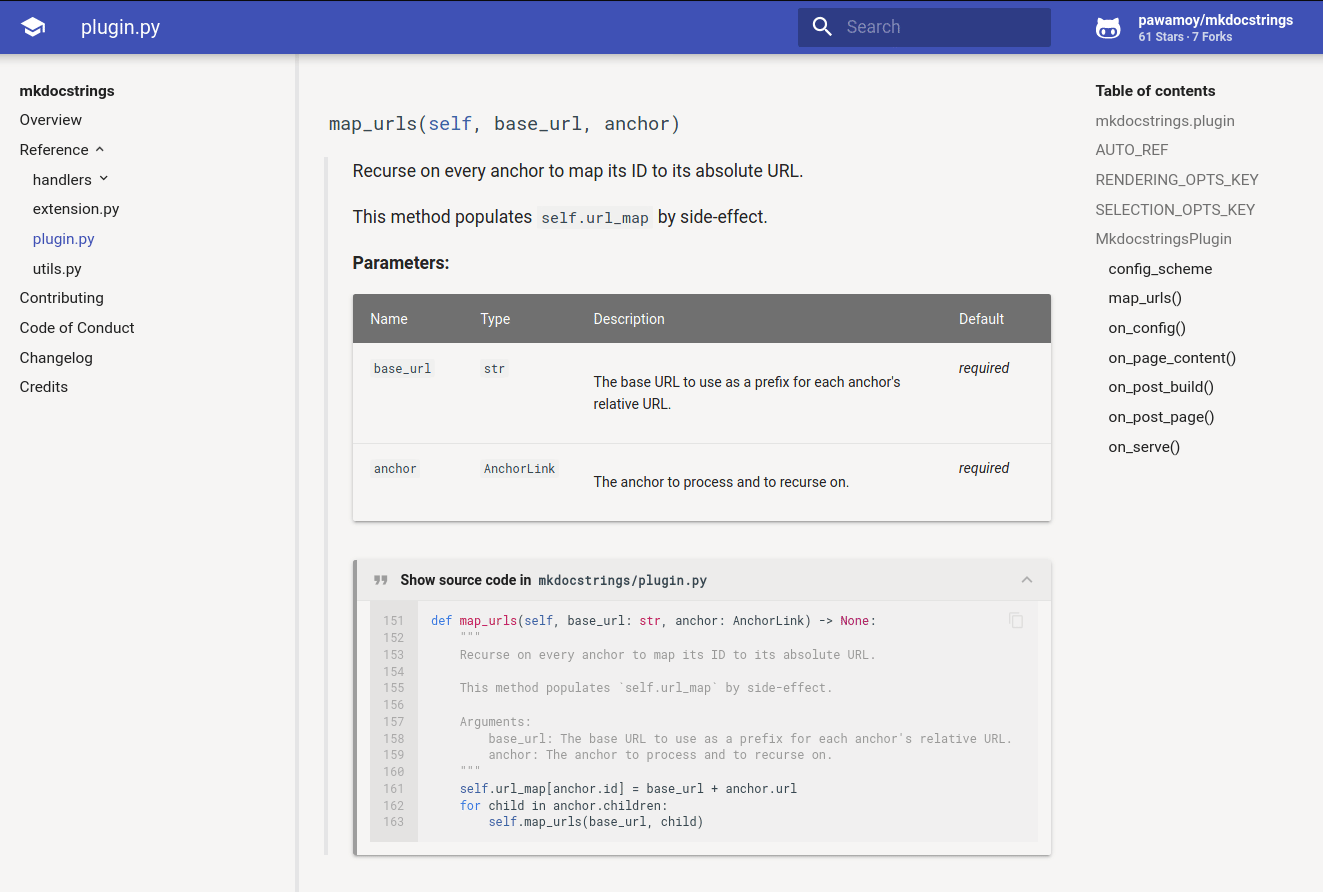
mkdocstringscan add a collapsible div containing the highlighted source code of the Python object.
To get an example of what is possible, check mkdocstrings' own documentation, auto-generated from sources by itself of course, and the following GIF:
Roadmap
See the Feature Roadmap issue on the bugtracker.
Requirements
mkdocstrings requires Python 3.6 or above.
To install Python 3.6, I recommend using pyenv.
# install pyenv
git clone https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv ~/.pyenv
# setup pyenv (you should also put these three lines in .bashrc or similar)
export PATH="${HOME}/.pyenv/bin:${PATH}"
export PYENV_ROOT="${HOME}/.pyenv"
eval "$(pyenv init -)"
# install Python 3.6
pyenv install 3.6.12
# make it available globally
pyenv global system 3.6.12
This project currently only works with the Material theme of MkDocs. Therefore, it is required that you have it installed.
pip install mkdocs-material
Installation
With pip:
python3.6 -m pip install mkdocstrings
With conda:
conda install -c conda-forge mkdocstrings
Quick usage
# mkdocs.yml
theme:
name: "material"
plugins:
- search
- mkdocstrings
In one of your markdown files:
# Reference
::: my_library.my_module.my_class
See the Usage section of the docs for more examples!