combo: A Python Toolbox for Machine Learning Model Combination
Deployment & Documentation & Stats



Build Status & Coverage & Maintainability & License

combo is a comprehensive Python toolbox for combining machine learning (ML) models and scores. Model combination can be considered as a subtask of ensemble learning, and has been widely used in real-world tasks and data science competitions like Kaggle [3]. combo has been used/introduced in various research works since its inception [7] [11].
combo library supports the combination of models and score from key ML libraries such as scikit-learn, xgboost, and LightGBM, for crucial tasks including classification, clustering, anomaly detection. See figure below for some representative combination approaches.
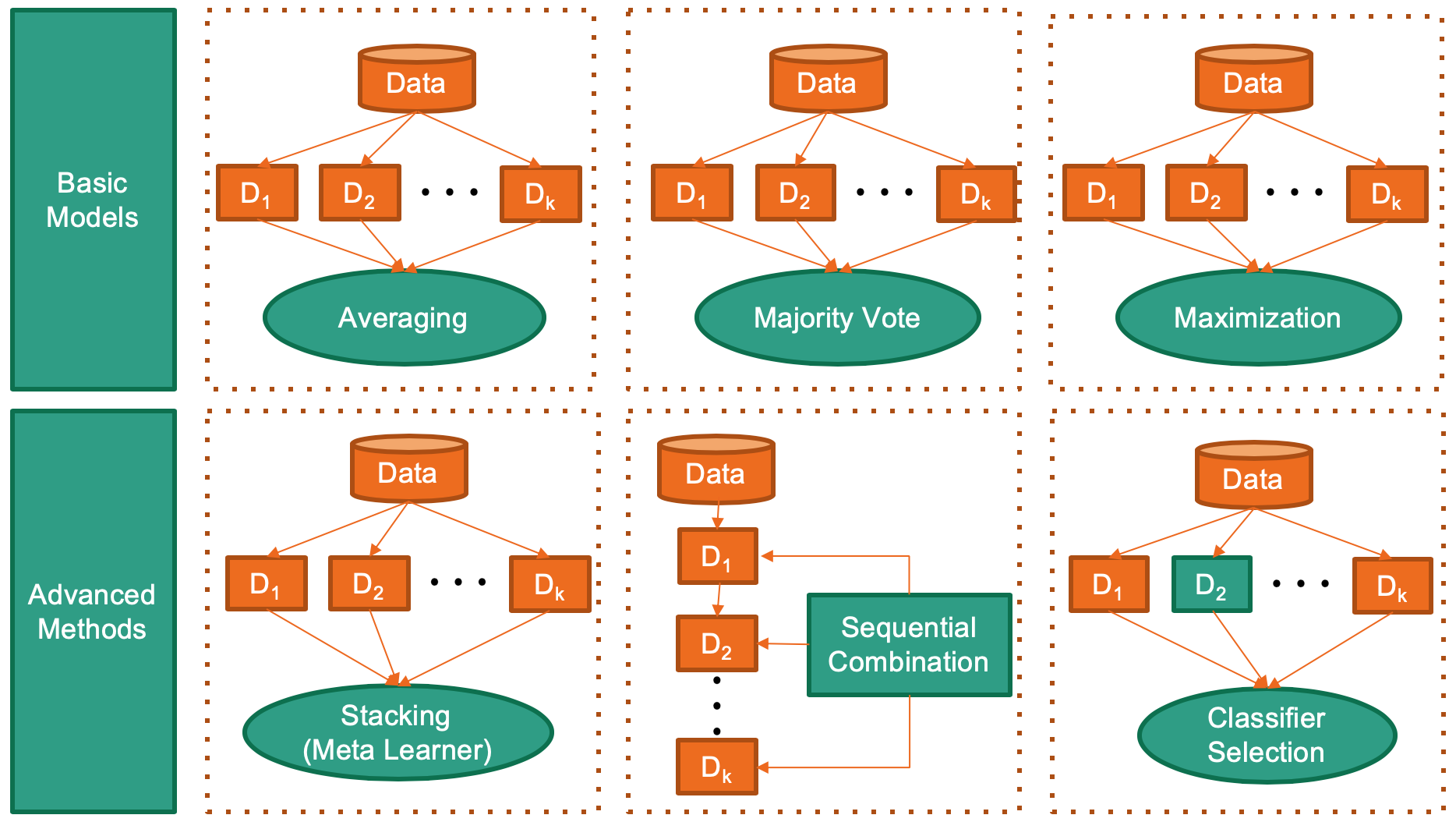
combo is featured for:
- Unified APIs, detailed documentation, and interactive examples across various algorithms.
- Advanced and latest models, such as Stacking/DCS/DES/EAC/LSCP.
- Comprehensive coverage for classification, clustering, anomaly detection, and raw score.
- Optimized performance with JIT and parallelization when possible, using numba and joblib.
API Demo:
from combo.models.classifier_stacking import Stacking
# initialize a group of base classifiers
classifiers = [DecisionTreeClassifier(), LogisticRegression(),
KNeighborsClassifier(), RandomForestClassifier(),
GradientBoostingClassifier()]
clf = Stacking(base_estimators=classifiers) # initialize a Stacking model
clf.fit(X_train, y_train) # fit the model
# predict on unseen data
y_test_labels = clf.predict(X_test) # label prediction
y_test_proba = clf.predict_proba(X_test) # probability prediction
Citing combo:
combo paper is published in AAAI 2020 (demo track). If you use combo in a scientific publication, we would appreciate citations to the following paper:
@inproceedings{zhao2020combo,
title={Combining Machine Learning Models and Scores using combo library},
author={Zhao, Yue and Wang, Xuejian and Cheng, Cheng and Ding, Xueying},
booktitle={Thirty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
month = {Feb},
year={2020},
address = {New York, USA}
}
or:
Zhao, Y., Wang, X., Cheng, C. and Ding, X., 2020. Combining Machine Learning Models and Scores using combo library. Thirty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence.
Key Links and Resources:
- awesome-ensemble-learning (ensemble learning related books, papers, and more)
- View the latest codes on Github
- View the documentation & API
- View all examples
- View the demo video for AAAI 2020
- Execute Interactive Jupyter Notebooks
Table of Contents:
- Installation
- API Cheatsheet & Reference
- Implemented Algorithms
- Example 1: Classifier Combination with Stacking/DCS/DES
- Example 2: Simple Classifier Combination
- Example 3: Clustering Combination
- Example 4: Outlier Detector Combination
- Development Status
- Inclusion Criteria
Installation
It is recommended to use pip for installation. Please make sure the latest version is installed, as combo is updated frequently:
pip install combo # normal install
pip install --upgrade combo # or update if needed
pip install --pre combo # or include pre-release version for new features
Alternatively, you could clone and run setup.py file:
git clone https://github.com/yzhao062/combo.git
cd combo
pip install .
Required Dependencies:
- Python 3.5, 3.6, or 3.7
- joblib
- matplotlib (optional for running examples)
- numpy>=1.13
- numba>=0.35
- pyod
- scipy>=0.19.1
- scikit_learn>=0.20
Note on Python 2: The maintenance of Python 2.7 will be stopped by January 1, 2020 (see official announcement). To be consistent with the Python change and combo's dependent libraries, e.g., scikit-learn, combo only supports Python 3.5+ and we encourage you to use Python 3.5 or newer for the latest functions and bug fixes. More information can be found at Moving to require Python 3.
API Cheatsheet & Reference
Full API Reference: (https://pycombo.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api.html). The following APIs are consistent for most of the models (API Cheatsheet: https://pycombo.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api_cc.html).
- fit(X, y): Fit estimator. y is optional for unsupervised methods.
- predict(X): Predict on a particular sample once the estimator is fitted.
- predict_proba(X): Predict the probability of a sample belonging to each class once the estimator is fitted.
- fit_predict(X, y): Fit estimator and predict on X. y is optional for unsupervised methods.
For raw score combination (after the score matrix is generated), use individual methods from "score_comb.py" directly. Raw score combination API: (https://pycombo.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api.html#score-combination).
Implemented Algorithms
combo groups combination frameworks by tasks. General purpose methods are fundamental ones which can be applied to various tasks.
| Task | Algorithm | Year | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Purpose | Average & Weighted Average: average across all scores/prediction results, maybe with weights | N/A | [13] |
| General Purpose | Maximization: simple combination by taking the maximum scores | N/A | [13] |
| General Purpose | Median: take the median value across all scores/prediction results | N/A | [13] |
| General Purpose | Majority Vote & Weighted Majority Vote | N/A | [13] |
| Classification | SimpleClassifierAggregator: combining classifiers by general purpose methods above | N/A | N/A |
| Classification | DCS: Dynamic Classifier Selection (Combination of multiple classifiers using local accuracy estimates) | 1997 | [8] |
| Classification | DES: Dynamic Ensemble Selection (From dynamic classifier selection to dynamic ensemble selection) | 2008 | [5] |
| Classification | Stacking (meta ensembling): use a meta learner to learn the base classifier results | N/A | [4] |
| Clustering | Clusterer Ensemble: combine the results of multiple clustering results by relabeling | 2006 | [12] |
| Clustering | Combining multiple clusterings using evidence accumulation (EAC) | 2002 | [6] |
| Anomaly Detection | SimpleDetectorCombination: combining outlier detectors by general purpose methods above | N/A | [2] |
| Anomaly Detection | Average of Maximum (AOM): divide base detectors into subgroups to take the maximum, and then average | 2015 | [1] |
| Anomaly Detection | Maximum of Average (MOA): divide base detectors into subgroups to take the average, and then maximize | 2015 | [1] |
| Anomaly Detection | XGBOD: a semi-supervised combination framework for outlier detection | 2018 | [9] |
| Anomaly Detection | Locally Selective Combination (LSCP) | 2019 | [10] |
The comparison among selected implemented models is made available below (Figure, compare_selected_classifiers.py, Interactive Jupyter Notebooks). For Jupyter Notebooks, please navigate to "/notebooks/compare_selected_classifiers.ipynb".
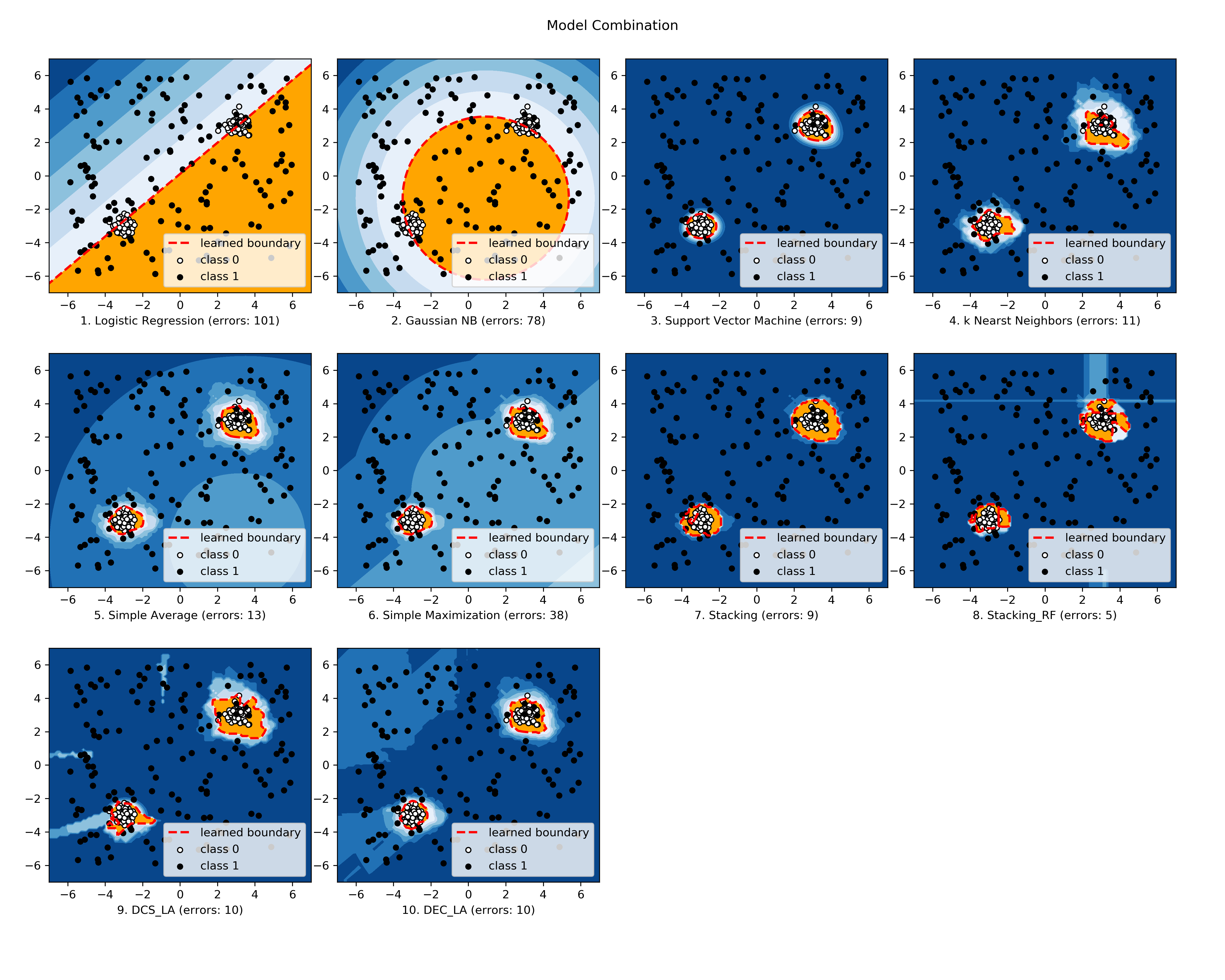
All implemented modes are associated with examples, check "combo examples" for more information.
Example of Stacking/DCS/DES
"examples/classifier_stacking_example.py" demonstrates the basic API of stacking (meta ensembling). "examples/classifier_dcs_la_example.py" demonstrates the basic API of Dynamic Classifier Selection by Local Accuracy. "examples/classifier_des_la_example.py" demonstrates the basic API of Dynamic Ensemble Selection by Local Accuracy.
It is noted the basic API is consistent across all these models.
Initialize a group of classifiers as base estimators
# initialize a group of classifiers classifiers = [DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=random_state), LogisticRegression(random_state=random_state), KNeighborsClassifier(), RandomForestClassifier(random_state=random_state), GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=random_state)]
Initialize, fit, predict, and evaluate with Stacking
from combo.models.classifier_stacking import Stacking clf = Stacking(base_estimators=classifiers, n_folds=4, shuffle_data=False, keep_original=True, use_proba=False, random_state=random_state) clf.fit(X_train, y_train) y_test_predict = clf.predict(X_test) evaluate_print('Stacking | ', y_test, y_test_predict)
See a sample output of classifier_stacking_example.py
Decision Tree | Accuracy:0.9386, ROC:0.9383, F1:0.9521 Logistic Regression | Accuracy:0.9649, ROC:0.9615, F1:0.973 K Neighbors | Accuracy:0.9561, ROC:0.9519, F1:0.9662 Gradient Boosting | Accuracy:0.9605, ROC:0.9524, F1:0.9699 Random Forest | Accuracy:0.9605, ROC:0.961, F1:0.9693 Stacking | Accuracy:0.9868, ROC:0.9841, F1:0.9899
Example of Classifier Combination
"examples/classifier_comb_example.py" demonstrates the basic API of predicting with multiple classifiers. It is noted that the API across all other algorithms are consistent/similar.
Initialize a group of classifiers as base estimators
# initialize a group of classifiers classifiers = [DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=random_state), LogisticRegression(random_state=random_state), KNeighborsClassifier(), RandomForestClassifier(random_state=random_state), GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=random_state)]
Initialize, fit, predict, and evaluate with a simple aggregator (average)
from combo.models.classifier_comb import SimpleClassifierAggregator clf = SimpleClassifierAggregator(classifiers, method='average') clf.fit(X_train, y_train) y_test_predicted = clf.predict(X_test) evaluate_print('Combination by avg |', y_test, y_test_predicted)
See a sample output of classifier_comb_example.py
Decision Tree | Accuracy:0.9386, ROC:0.9383, F1:0.9521 Logistic Regression | Accuracy:0.9649, ROC:0.9615, F1:0.973 K Neighbors | Accuracy:0.9561, ROC:0.9519, F1:0.9662 Gradient Boosting | Accuracy:0.9605, ROC:0.9524, F1:0.9699 Random Forest | Accuracy:0.9605, ROC:0.961, F1:0.9693 Combination by avg | Accuracy:0.9693, ROC:0.9677, F1:0.9763 Combination by w_avg | Accuracy:0.9781, ROC:0.9716, F1:0.9833 Combination by max | Accuracy:0.9518, ROC:0.9312, F1:0.9642 Combination by w_vote| Accuracy:0.9649, ROC:0.9644, F1:0.9728 Combination by median| Accuracy:0.9693, ROC:0.9677, F1:0.9763
Example of Clustering Combination
"examples/cluster_comb_example.py" demonstrates the basic API of combining multiple base clustering estimators. "examples/cluster_eac_example.py" demonstrates the basic API of Combining multiple clusterings using evidence accumulation (EAC).
Initialize a group of clustering methods as base estimators
# Initialize a set of estimators estimators = [KMeans(n_clusters=n_clusters), MiniBatchKMeans(n_clusters=n_clusters), AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=n_clusters)]
Initialize a Clusterer Ensemble class and fit the model
from combo.models.cluster_comb import ClustererEnsemble # combine by Clusterer Ensemble clf = ClustererEnsemble(estimators, n_clusters=n_clusters) clf.fit(X)
Get the aligned results
# generate the labels on X aligned_labels = clf.aligned_labels_ predicted_labels = clf.labels_
Example of Outlier Detector Combination
"examples/detector_comb_example.py" demonstrates the basic API of combining multiple base outlier detectors.
Initialize a group of outlier detection methods as base estimators
# Initialize a set of estimators detectors = [KNN(), LOF(), OCSVM()]
Initialize a simple averaging aggregator, fit the model, and make the prediction.
from combo.models.detector combination import SimpleDetectorAggregator clf = SimpleDetectorAggregator(base_estimators=detectors) clf_name = 'Aggregation by Averaging' clf.fit(X_train) y_train_pred = clf.labels_ # binary labels (0: inliers, 1: outliers) y_train_scores = clf.decision_scores_ # raw outlier scores # get the prediction on the test data y_test_pred = clf.predict(X_test) # outlier labels (0 or 1) y_test_scores = clf.decision_function(X_test) # outlier scores
Evaluate the prediction using ROC and Precision @ Rank n.
# evaluate and print the results print("\nOn Training Data:") evaluate_print(clf_name, y_train, y_train_scores) print("\nOn Test Data:") evaluate_print(clf_name, y_test, y_test_scores)
See sample outputs on both training and test data.
On Training Data: Aggregation by Averaging ROC:0.9994, precision @ rank n:0.95 On Test Data: Aggregation by Averaging ROC:1.0, precision @ rank n:1.0
Development Status
combo is currently under development as of Feb, 2020. A concrete plan has been laid out and will be implemented in the next few months.
Similar to other libraries built by us, e.g., Python Outlier Detection Toolbox (pyod), combo is also targeted to be published in Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR), open-source software track. A demo paper has been presented in AAAI 2020 for progress update.
Watch & Star to get the latest update! Also feel free to send me an email ([email protected]) for suggestions and ideas.
Inclusion Criteria
Similarly to scikit-learn, We mainly consider well-established algorithms for inclusion. A rule of thumb is at least two years since publication, 50+ citations, and usefulness.
However, we encourage the author(s) of newly proposed models to share and add your implementation into combo for boosting ML accessibility and reproducibility. This exception only applies if you could commit to the maintenance of your model for at least two year period.
Reference
| [1] | (1, 2) Aggarwal, C.C. and Sathe, S., 2015. Theoretical foundations and algorithms for outlier ensembles. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 17(1), pp.24-47. |
| [2] | Aggarwal, C.C. and Sathe, S., 2017. Outlier ensembles: An introduction. Springer. |
| [3] | Bell, R.M. and Koren, Y., 2007. Lessons from the Netflix prize challenge. SIGKDD Explorations, 9(2), pp.75-79. |
| [4] | Gorman, B. (2016). A Kaggler's Guide to Model Stacking in Practice. [online] The Official Blog of Kaggle.com. Available at: http://blog.kaggle.com/2016/12/27/a-kagglers-guide-to-model-stacking-in-practice [Accessed 26 Jul. 2019]. |
| [5] | Ko, A.H., Sabourin, R. and Britto Jr, A.S., 2008. From dynamic classifier selection to dynamic ensemble selection. Pattern recognition, 41(5), pp.1718-1731. |
| [6] | Fred, A. L. N., & Jain, A. K. (2005). Combining multiple clusterings using evidence accumulation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 27(6), 835–850. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2005.113 |
| [7] | Raschka, S., Patterson, J. and Nolet, C., 2020. Machine Learning in Python: Main developments and technology trends in data science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.04803. |
| [8] | Woods, K., Kegelmeyer, W.P. and Bowyer, K., 1997. Combination of multiple classifiers using local accuracy estimates. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 19(4), pp.405-410. |
| [9] | Zhao, Y. and Hryniewicki, M.K. XGBOD: Improving Supervised Outlier Detection with Unsupervised Representation Learning. IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2018. |
| [10] | Zhao, Y., Nasrullah, Z., Hryniewicki, M.K. and Li, Z., 2019, May. LSCP: Locally selective combination in parallel outlier ensembles. In Proceedings of the 2019 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SDM), pp. 585-593. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics. |
| [11] | Zhao, Y., Nasrullah, Z. and Li, Z., 2019. PyOD: A Python Toolbox for Scalable Outlier Detection. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 20, pp.1-7. |
| [12] | Zhou, Z.H. and Tang, W., 2006. Clusterer ensemble. Knowledge-Based Systems, 19(1), pp.77-83. |
| [13] | (1, 2, 3, 4) Zhou, Z.H., 2012. Ensemble methods: foundations and algorithms. Chapman and Hall/CRC. |