Getting-Started-with-Docker-and-Flask
Introduction
Docker makes it easier, simpler and safer to build, deploy and manage applications in a docker container. This article will help you get a detailed understanding of;
- What is docker?
- Why use Docker?
- What is a docker image?
- What is a docker container?
- Dockerizing a flask application
What is Docker?
Docker is an open source containerization platform for developing, shipping and running applications.
Docker packages software into standardized units called containers. Containers have everything the software needs to run including libraries, system tools, code, and runtime.
Why use Docker?
- Responsive deployment and scaling.
- Faster And Consistent Delivery Of Applications.
Docker image.
Image is a read-only template with instruction for creating containers. Docker images can be considered as the blueprint of the entire application environment that you create.
Docker container.
- A Docker container is a virtualized run-time environment where users can isolate applications from the underlying system.
- Containers are compact, portable units in which you can start up an application quickly and easily.
- Docker containers contains all the essential things required to run an application like code, runtime, system tools, system libraries, and settings.
Dockerizing a flask application
File structure and setup
\-- dockerExample
|-- app.py
|-- Dockerfile
|-- requirements.txt
\-- templates
|-- index.html
First I created a simple Flask application and added the following code to app.py.
from flask import Flask,render_template
app=Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def home():
return render_template('index.html')
if __name__==('__main__'):
app.run(debug=True)
Check how to create a simple flask application
Add the following code to index.html
>
<html>
<head>
<title>Getting started with Dockertitle>
head>
<body>
<p>This is my Dockerfilep>
body>
Now we need to dockerize the flask application by creating a Dockerfile Dockerfileis a text document that contains all the commands a user could call on the command line to assemble an image.
Add the following code to docker;
FROM python:3.9.6
COPY . /doc
COPY ./requirements.txt /doc/requirements.txt
WORKDIR /doc
EXPOSE 5000:5000
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
CMD ["python","app.py"]
- FROM keyword is used to specify the base image to be used. We'll be making use of a python base image.
- WORKDIR defines the main directory of operations.
- EXPOSE informs Docker that the container listens on the specified network ports at runtime.
- RUN is used to install the project’s dependencies.
- CMD provide defaults for an executing container.
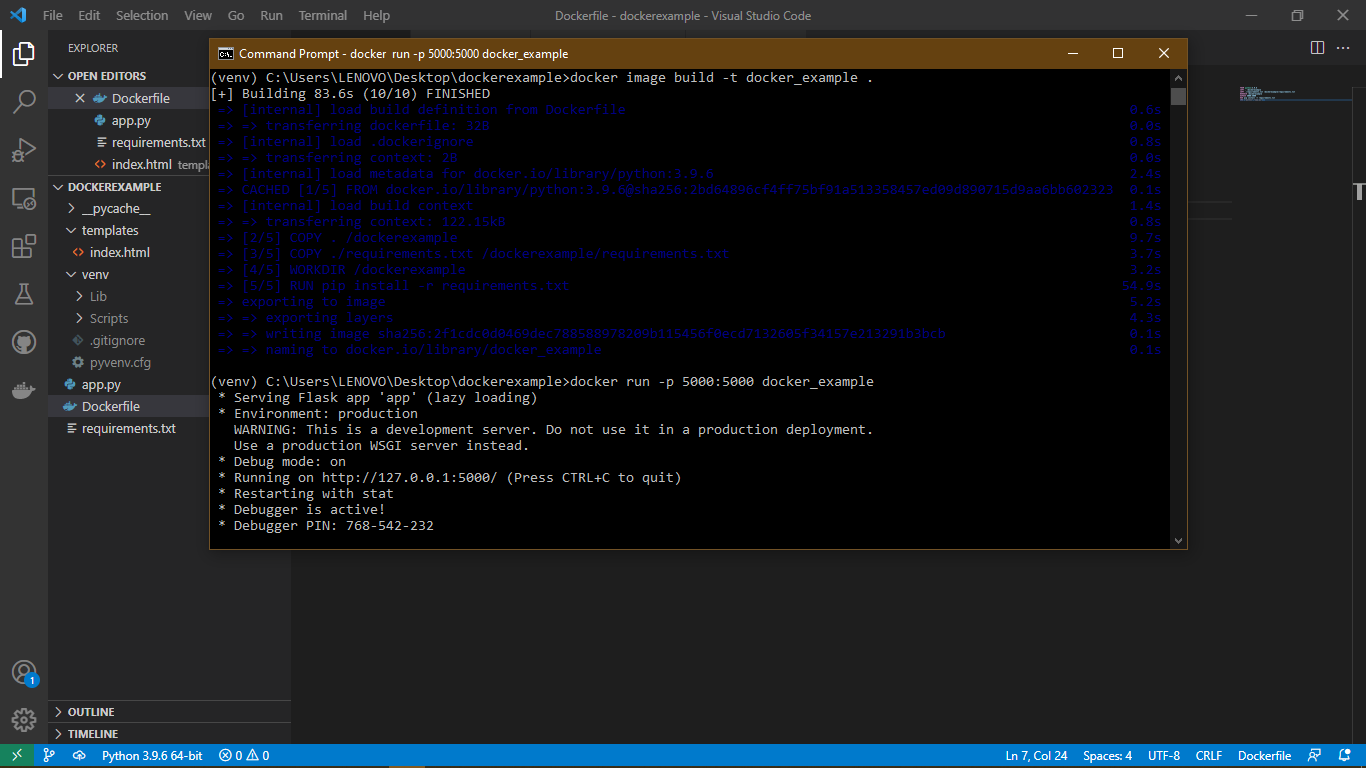
We can now build our image with the docker build command as shown below;
docker image build -t docker_example .
Once the build process is done, we can run the application with the docker run command as shown below;
docker run -p 5000:5000 docker_example