Breast Cancer Classification
Using SKLearn breast cancer dataset which contains 569 examples and 32 features classifying has been made with 6 different algorithms. The metrics below have been used to determine these algorithms performance.
- Accuracy
- Precision
- Recall
- F Score
Accuracy may produce misleading results so because of that I also added some metrics which some of them are more reliable (e.g. F Score).
Algorithms
Logistic regression, SVM (Support Vector Machines), decision trees, random forest, naive bayes, k-nearest neighbor algorithms have been used and for each of them metrics are calculated and results are shown.
Data Preprocessing
The dataset contains no missing rows or columns so we can start feature selection. To do that I used correlation map to show the correlation between features. And I eliminated mostly correlated features like perimeter_mean and perimeter_worst. After this process we have 18 features.
Then we apply data normalization and our data is ready for classification.
# Data normalization
standardizer = StandardScaler()
X = standardizer.fit_transform(X)
Train and Test Split
I have split my dataset as %30 test, % 70 training and set random_state parameter to 0 as shown.
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=0)
After splitting dataset, I created dictionaries for algorithms and metrics. And in one for loop every model trained and tested.
models = {'Logistic Regression': LogisticRegression(), 'Support Vector Machines': LinearSVC(),
'Decision Trees': DecisionTreeClassifier(), 'Random Forest': RandomForestClassifier(),
'Naive Bayes': GaussianNB(), 'K-Nearest Neighbor': KNeighborsClassifier()}
accuracy, precision, recall, f_score = {}, {}, {}, {}
for key in models.keys():
# Fit the classifier model
models[key].fit(X_train, y_train)
# Classification
classification = models[key].predict(X_test)
# Calculate Accuracy, Precision, Recall and F Score Metrics
accuracy[key] = accuracy_score(classification, y_test)
precision[key] = precision_score(classification, y_test)
recall[key] = recall_score(classification, y_test)
f_score[key] = f1_score(classification, y_test)
Results
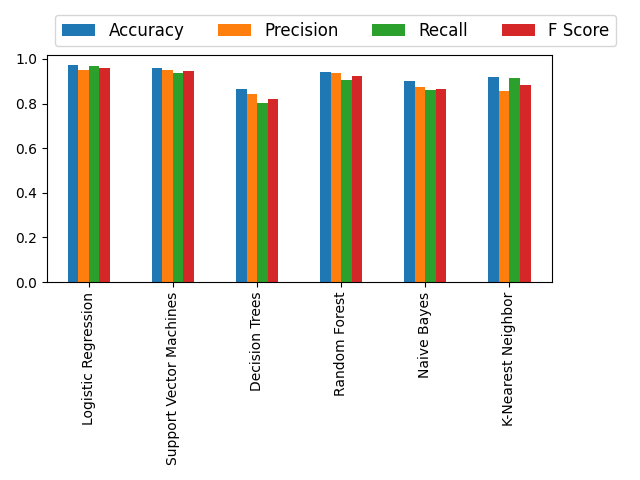
As you can see the figure below, most successful classification algorithm seems to logistic regression. And decision tress has the worst performance.
To see the values algorithms got for each metric see the table below.
| Algorithm | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Regression | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
| SVM | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.94 |
| Decision Trees | 0.86 | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.82 |
| Random Forest | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.92 |
| Naive Bayes | 0.90 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.86 |
| K-Nearest Neighbor | 0.91 | 0.85 | 0.91 | 0.88 |
Conclusion
I have tuned few parameters for example training and test size, random state and most of the algorithms performed close enough to each other. For different datasets this code can be used. You may need to change feature selection part and if your dataset has missing values you should fill in these values as well. Other than these things you can perform classification with different kind of algorithms.