Alfred
Alfred is command line tool for deep-learning usage. if you want split an video into image frames or combine frames into a single video, then alfred is what you want.
Install
To install alfred, it is very simple:
sudo pip3 install alfred-py
alfred is both a lib and a tool, you can import it's APIs, or you can directly call it inside your terminal.
A glance of alfred, after you installed above package, you will have alfred:
-
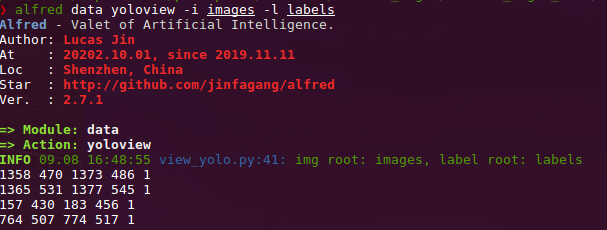
datamodule:# show VOC annotations alfred data vocview -i JPEGImages/ -l Annotations/ # show coco anntations alfred data cocoview -j annotations/instance_2017.json -i images/ # show yolo annotations alfred data yoloview -i images -l labels # show detection label with txt format alfred data txtview -i images/ -l txts/ # show more of data alfred data -h # eval tools alfred data evalvoc -h
-
cabmodule:# count files number of a type alfred cab count -d ./images -t jpg # split a txt file into train and test alfred cab split -f all.txt -r 0.9,0.1 -n train,val
-
visionmodule;# extract video to images alfred vision extract -v video.mp4 # combine images to video alfred vision 2video -d images/
-
-hto see more:usage: alfred [-h] [--version] {vision,text,scrap,cab,data} ... positional arguments: {vision,text,scrap,cab,data} vision vision related commands. text text related commands. scrap scrap related commands. cab cabinet related commands. data data related commands. optional arguments: -h, --help show this help message and exit --version, -v show version info.inside every child module, you can call it's
-has well:alfred text -h.
if you are on windows, you can install pycocotools via:
pip install "git+https://github.com/philferriere/cocoapi.git#egg=pycocotools&subdirectory=PythonAPI", we have made pycocotools as an dependencies since we need pycoco API.
Updates
alfred-py has been updating for 3 years, and it will keep going!
-
2050-xxx: to be continue;
-
2021.11.13: Now I add Siren SDK support!
from functools import wraps from alfred.siren.handler import SirenClient from alfred.siren.models import ChatMessage, InvitationMessage siren = SirenClient('daybreak_account', 'password') @siren.on_received_invitation def on_received_invitation(msg: InvitationMessage): print('received invitation: ', msg.invitation) # directly agree this invitation for robots @siren.on_received_chat_message def on_received_chat_msg(msg: ChatMessage): print('got new msg: ', msg.text) siren.publish_txt_msg('I got your message O(∩_∩)O哈哈~', msg.roomId) if __name__ == '__main__': siren.loop()Using this, you can easily setup a Chatbot. By using Siren client.
-
2021.06.24: Add a useful commandline tool, change your pypi source easily!!:
alfred cab changesourceAnd then your pypi will using aliyun by default!
-
2021.05.07: Upgrade Open3D instructions: Open3D>0.9.0 no longer compatible with previous alfred-py. Please upgrade Open3D, you can build Open3D from source:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/intel-isl/Open3D.git cd Open3D && mkdir build && cd build sudo apt install libc++abi-8-dev sudo apt install libc++-8-dev cmake .. -DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE=/usr/bin/python3Ubuntu 16.04 blow I tried all faild to build from source. So, please using open3d==0.9.0 for alfred-py.
-
2021.04.01: A unified evaluator had added. As all we know, for many users, writting Evaluation might coupled deeply with your project. But with Alfred's help, you can do evaluation in any project by simply writting 8 lines of codes, for example, if your dataset format is Yolo, then do this:
def infer_func(img_f): image = cv2.imread(img_f) results = config_dict['model'].predict_for_single_image( image, aug_pipeline=simple_widerface_val_pipeline, classification_threshold=0.89, nms_threshold=0.6, class_agnostic=True) if len(results) > 0: results = np.array(results)[:, [2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1]] # xywh to xyxy results[:, 2] += results[:, 0] results[:, 3] += results[:, 1] return results if __name__ == '__main__': conf_thr = 0.4 iou_thr = 0.5 imgs_root = 'data/hand/images' labels_root = 'data/hand/labels' yolo_parser = YoloEvaluator(imgs_root=imgs_root, labels_root=labels_root, infer_func=infer_func) yolo_parser.eval_precisely()
Then you can get your evaluation results automatically. All recall, precision, mAP will printed out. More dataset format are on-going.
-
2021.03.10: New added
ImageSourceIterclass, when you want write a demo of your project which need to handle any input such as image file / folder / video file etc. You can usingImageSourceIter:from alfred.utils.file_io import ImageSourceIter # data_f can be image_file or image_folder or video iter = ImageSourceIter(ops.test_path) while True: itm = next(iter) if isinstance(itm, str): itm = cv2.imread(itm) # cv2.imshow('raw', itm) res = detect_for_pose(itm, det_model) cv2.imshow('res', itm) if iter.video_mode: cv2.waitKey(1) else: cv2.waitKey(0)
And then you can avoid write anything else of deal with file glob or reading video in cv. note that itm return can be a cv array or a file path.
-
2021.01.25: alfred now support self-defined visualization on coco format annotation (not using pycoco tools):
If your dataset in coco format but visualize wrongly pls fire a issue to me, thank u!
-
2020.09.27: Now, yolo and VOC can convert to each other, so that using Alfred you can:
- convert yolo2voc;
- convert voc2yolo;
- convert voc2coco;
- convert coco2voc;
By this, you can convert any labeling format of each other.
-
2020.09.08: After a long time past, alfred got some updates: We providing
coco2yoloability inside it. Users can run this command convert your data to yolo format:alfred data coco2yolo -i images/ -j annotations/val_split_2020.jsonOnly should provided is your image root path and your json file. And then all result will generated into
yolofolder under images or in images parent dir.After that (you got your yolo folder), then you can visualize the conversion result to see if it correct or not:
alfred data yolovview -i images/ -l labels/ -
2020.07.27: After a long time past, alfred finally get some updates:
Now, you can using alfred draw Chinese charactors on image without xxxx undefined encodes.
from alfred.utils.cv_wrapper import put_cn_txt_on_img img = put_cn_txt_on_img(img, spt[-1], [points[0][0], points[0][1]-25], 1.0, (255, 255, 255))
Also, you now can merge 2 VOC datasets! This is helpful when you have 2 dataset and you want merge them into a single one.
alfred data mergevoc -hYou can see more promotes.
-
2020.03.08:Several new files added in alfred:
alfred.utils.file_io: Provide file io utils for common purpose alfred.dl.torch.env: Provide seed or env setup in pytorch (same API as detectron2) alfred.dl.torch.distribute: utils used for distribute training when using pytorch -
2020.03.04: We have added some evaluation tool to calculate mAP for object detection model performance evaluation, it's useful and can visualize result:
this usage is also quite simple:
alfred data evalvoc -g ground-truth -d detection-results -im imageswhere
-gis your ground truth dir (contains xmls or txts),-dis your detection result files dir,-imis your images fodler. You only need save all your detected results into txts, one image one txt, and format like this:bottle 0.14981 80 1 295 500 bus 0.12601 36 13 404 316 horse 0.12526 430 117 500 307 pottedplant 0.14585 212 78 292 118 tvmonitor 0.070565 388 89 500 196
-
2020.02.27: We just update a
licensemodule inside alfred, say you want apply license to your project or update license, simple:alfred cab license -o 'MANA' -n 'YoloV3' -u 'manaai.cn'
you can found more detail usage with
alfred cab license -h -
2020-02-11: open3d has changed their API. we have updated new open3d inside alfred, you can simply using latest open3d and run
python3 examples/draw_3d_pointcloud.pyyou will see this: -
2020-02-10: alfred now support windows (experimental);
-
2020-02-01: 武汉加油! alfred fix windows pip install problem related to encoding 'gbk';
-
2020-01-14: Added cabinet module, also add some utils under data module;
-
2019-07-18: 1000 classes imagenet labelmap added. Call it from:
from alfred.vis.image.get_dataset_label_map import imagenet_labelmap # also, coco, voc, cityscapes labelmap were all added in from alfred.vis.image.get_dataset_label_map import coco_labelmap from alfred.vis.image.get_dataset_label_map import voc_labelmap from alfred.vis.image.get_dataset_label_map import cityscapes_labelmap
-
2019-07-13: We add a VOC check module in command line usage, you can now visualize your VOC format detection data like this:
alfred data voc_view -i ./images -l labels/ -
2019-05-17: We adding open3d as a lib to visual 3d point cloud in python. Now you can do some simple preparation and visual 3d box right on lidar points and show like opencv!!
You can achieve this by only using alfred-py and open3d!
example code can be seen under
examples/draw_3d_pointcloud.py. code updated with latest open3d API!. -
2019-05-10: A minor updates but really useful which we called mute_tf, do you want to disable tensorflow ignoring log? simply do this!!
from alfred.dl.tf.common import mute_tf mute_tf() import tensorflow as tf
Then, the logging message were gone....
-
2019-05-07: Adding some protos, now you can parsing tensorflow coco labelmap by using alfred:
from alfred.protos.labelmap_pb2 import LabelMap from google.protobuf import text_format with open('coco.prototxt', 'r') as f: lm = LabelMap() lm = text_format.Merge(str(f.read()), lm) names_list = [i.display_name for i in lm.item] print(names_list)
-
2019-04-25: Adding KITTI fusion, now you can get projection from 3D label to image like this: we will also add more fusion utils such as for nuScene dataset.
We providing kitti fusion kitti for convert
camera link 3d pointsto image pixel, and convertlidar link 3d pointsto image pixel. Roughly going through of APIs like this:# convert lidar prediction to image pixel from alfred.fusion.kitti_fusion import LidarCamCalibData, \ load_pc_from_file, lidar_pts_to_cam0_frame, lidar_pt_to_cam0_frame from alfred.fusion.common import draw_3d_box, compute_3d_box_lidar_coords # consit of prediction of lidar # which is x,y,z,h,w,l,rotation_y res = [[4.481686, 5.147319, -1.0229858, 1.5728549, 3.646751, 1.5121397, 1.5486346], [-2.5172017, 5.0262384, -1.0679419, 1.6241353, 4.0445814, 1.4938312, 1.620804], [1.1783253, -2.9209857, -0.9852259, 1.5852798, 3.7360613, 1.4671413, 1.5811548]] for p in res: xyz = np.array([p[: 3]]) c2d = lidar_pt_to_cam0_frame(xyz, frame_calib) if c2d is not None: cv2.circle(img, (int(c2d[0]), int(c2d[1])), 3, (0, 255, 255), -1) hwl = np.array([p[3: 6]]) r_y = [p[6]] pts3d = compute_3d_box_lidar_coords(xyz, hwl, angles=r_y, origin=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5), axis=2) pts2d = [] for pt in pts3d[0]: coords = lidar_pt_to_cam0_frame(pt, frame_calib) if coords is not None: pts2d.append(coords[:2]) pts2d = np.array(pts2d) draw_3d_box(pts2d, img)
And you can see something like this:
note:
compute_3d_box_lidar_coordsfor lidar prediction,compute_3d_box_cam_coordsfor KITTI label, cause KITTI label is based on camera coordinates!.since many users ask me how to reproduces this result, you can checkout demo file under
examples/draw_3d_box.py; -
2019-01-25: We just adding network visualization tool for pytorch now!! How does it look? Simply print out every layer network with output shape, I believe this is really helpful for people to visualize their models!
➜ mask_yolo3 git:(master) ✗ python3 tests.py ---------------------------------------------------------------- Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================ Conv2d-1 [-1, 64, 224, 224] 1,792 ReLU-2 [-1, 64, 224, 224] 0 ......... Linear-35 [-1, 4096] 16,781,312 ReLU-36 [-1, 4096] 0 Dropout-37 [-1, 4096] 0 Linear-38 [-1, 1000] 4,097,000 ================================================================ Total params: 138,357,544 Trainable params: 138,357,544 Non-trainable params: 0 ---------------------------------------------------------------- Input size (MB): 0.19 Forward/backward pass size (MB): 218.59 Params size (MB): 527.79 Estimated Total Size (MB): 746.57 ----------------------------------------------------------------Ok, that is all. what you simply need to do is:
from alfred.dl.torch.model_summary import summary from alfred.dl.torch.common import device from torchvision.models import vgg16 vgg = vgg16(pretrained=True) vgg.to(device) summary(vgg, input_size=[224, 224])
Support you input (224, 224) image, you will got this output, or you can change any other size to see how output changes. (currently not support for 1 channel image)
-
2018-12-7: Now, we adding a extensible class for quickly write an image detection or segmentation demo.
If you want write a demo which do inference on an image or an video or right from webcam, now you can do this in standared alfred way:
class ENetDemo(ImageInferEngine): def __init__(self, f, model_path): super(ENetDemo, self).__init__(f=f) self.target_size = (512, 1024) self.model_path = model_path self.num_classes = 20 self.image_transform = transforms.Compose( [transforms.Resize(self.target_size), transforms.ToTensor()]) self._init_model() def _init_model(self): self.model = ENet(self.num_classes).to(device) checkpoint = torch.load(self.model_path) self.model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict']) print('Model loaded!') def solve_a_image(self, img): images = Variable(self.image_transform(Image.fromarray(img)).to(device).unsqueeze(0)) predictions = self.model(images) _, predictions = torch.max(predictions.data, 1) prediction = predictions.cpu().numpy()[0] - 1 return prediction def vis_result(self, img, net_out): mask_color = np.asarray(label_to_color_image(net_out, 'cityscapes'), dtype=np.uint8) frame = cv2.resize(img, (self.target_size[1], self.target_size[0])) # mask_color = cv2.resize(mask_color, (frame.shape[1], frame.shape[0])) res = cv2.addWeighted(frame, 0.5, mask_color, 0.7, 1) return res if __name__ == '__main__': v_f = '' enet_seg = ENetDemo(f=v_f, model_path='save/ENet_cityscapes_mine.pth') enet_seg.run()
After that, you can directly inference from video. This usage can be found at git repo:
The repo using alfred: http://github.com/jinfagang/pt_enet
-
2018-11-6: I am so glad to announce that alfred 2.0 released!
😄 ⛽️ 👏 👏 Let's have a quick look what have been updated:# 2 new modules, fusion and vis from alred.fusion import fusion_utilsFor the module
fusioncontains many useful sensor fusion helper functions you may use, such as project lidar point cloud onto image. -
2018-08-01: Fix the video combined function not work well with sequence. Add a order algorithm to ensure video sequence right. also add some draw bbox functions into package.
can be called like this:
-
2018-03-16: Slightly update alfred, now we can using this tool to combine a video sequence back original video! Simply do:
# alfred binary exectuable program alfred vision 2video -d ./video_images
Capable
alfred is both a library and a command line tool. It can do those things:
# extract images from video
alfred vision extract -v video.mp4
# combine image sequences into a video
alfred vision 2video -d /path/to/images
# get faces from images
alfred vision getface -d /path/contains/images/
Just try it out!!
Copyright
Alfred build by Lucas Jin with jintianiloveu, this code released under MIT license.