ipylivebash
ipylivebash is a library to run shell script in Jupyter with live output.
Example
%%livebash --save log.txt --save-timestamp
find .
Run find . and show the output in the Jupyter notebook and also save to log-${current_timestamp}.txt
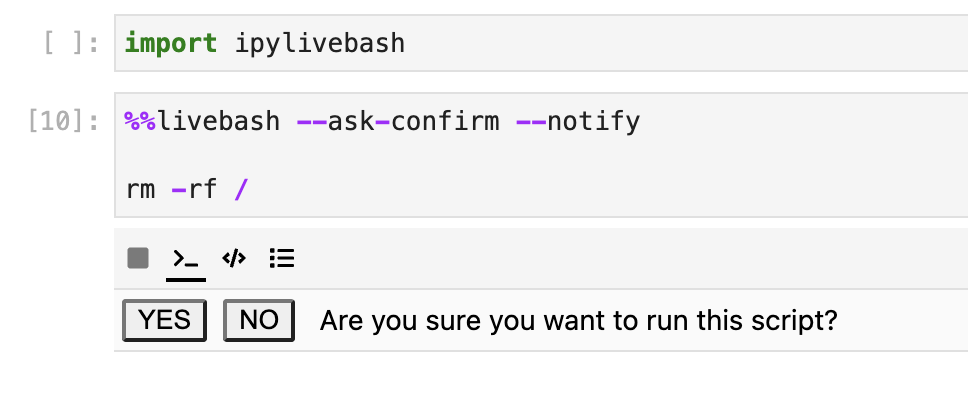
%%livebash --ask-confirm --notify
set -e
deploy_script
Before running the deploy_script show a panel to ask for confirmation. Once it is finished, show a notification.
Features
- Run shell script in Jupyter with live output
- The output in the notebook cell is not saved in the notebook by default
- Support to save the output to a file. If the file already exists, it will pick another name automatically.
- Support to show a confirmation UI before executing the script
- Support to send a notification when the script finishes.
Usage
usage: livebash [-h] [--save OUTPUT_FILE] [--save-timestamp]
[--line-limit LINE_LIMIT] [--height HEIGHT] [--ask-confirm]
[--notify] [--keep-cell-output]
optional arguments:
-h, --help
--save OUTPUT_FILE Save output to a file
--save-timestamp Add timestamp to the output file name
--line-limit LINE_LIMIT
Restrict the no. of lines to be shown
--height HEIGHT Set the height of the output cell
--ask-confirm Ask for confirmation before execution
--notify Send a notification when the script finished
--keep-cell-output Keep the cell output
Options
--save OUTPUT_FILE
Save the output to a file.
If the file name already exists, it will add a suffix to avoid overriding the original file.
--save-timestamp
Add timestamp to the output file name.
--line-limit LINE_LIMIT
If the no. of line output exceed the limit, it may be truncated. It will show the last 5 lines only.
--height HEIGHT
Set the height of the output cell
--ask-confirm
Ask for confirmation before execution
--notify
Send a notification when the script finished
--keep-cell-output
Keep the cell output such that it could be saved together with the notebook. It can't be used with other options like --line-limit.
Installation
You can install using pip:
pip install ipylivebash
If you are using Jupyter Notebook 5.2 or earlier, you may also need to enable the nbextension:
jupyter nbextension enable --py [--sys-prefix|--user|--system] ipylivebash
Development Installation
Create a dev environment:
conda create -n ipylivebash-dev -c conda-forge nodejs yarn python jupyterlab
conda activate ipylivebash-dev
Install the python. This will also build the TS package.
pip install -e ".[test, examples]"
When developing your extensions, you need to manually enable your extensions with the notebook / lab frontend. For lab, this is done by the command:
jupyter labextension develop --overwrite .
yarn run build
For classic notebook, you need to run:
jupyter nbextension install --sys-prefix --symlink --overwrite --py ipylivebash
jupyter nbextension enable --sys-prefix --py ipylivebash
Note that the --symlink flag doesn't work on Windows, so you will here have to run the install command every time that you rebuild your extension. For certain installations you might also need another flag instead of --sys-prefix, but we won't cover the meaning of those flags here.
How to see your changes
Typescript:
If you use JupyterLab to develop then you can watch the source directory and run JupyterLab at the same time in different terminals to watch for changes in the extension's source and automatically rebuild the widget.
# Watch the source directory in one terminal, automatically rebuilding when needed
yarn run watch
# Run JupyterLab in another terminal
jupyter lab
After a change wait for the build to finish and then refresh your browser and the changes should take effect.
Python:
If you make a change to the python code then you will need to restart the notebook kernel to have it take effect.