ClassyConf
ClassyConf is the configuration architecture solution for perfectionists with deadlines.
It provides a declarative way to define settings for your projects contained in a class that can be extended, overriden at runtime, config objects can be passed around modules and settings are lazily loaded, plus some other goodies.
You can find out more documentation at Read the Docs website, and the intro post here to understand the motivations behind it.
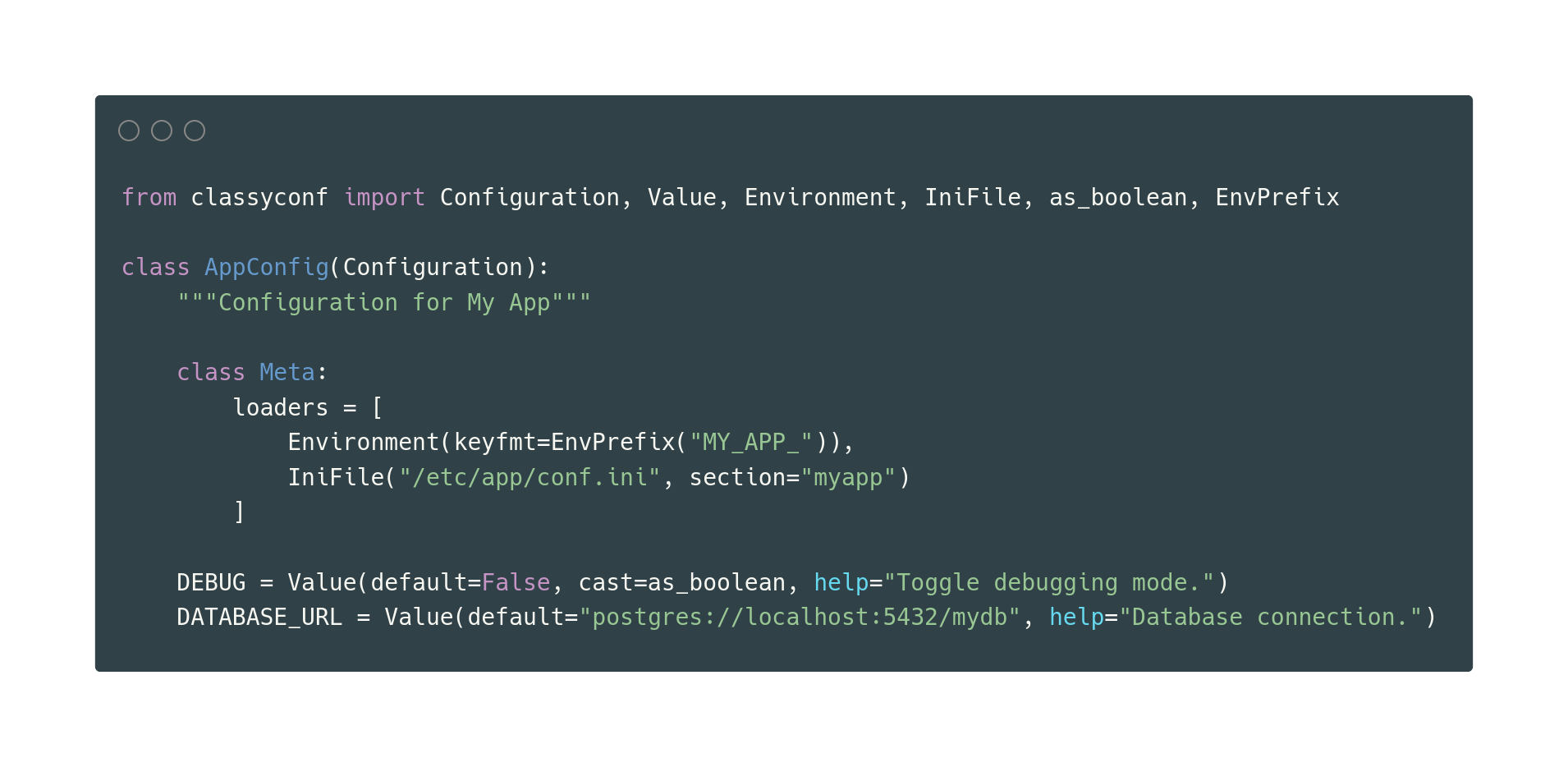
Here is a preview of how to use it:
from classyconf import Configuration, Value, Environment, IniFile, as_boolean, EnvPrefix
class AppConfig(Configuration):
"""Configuration for My App"""
class Meta:
loaders = [
Environment(keyfmt=EnvPrefix("MY_APP_")),
IniFile("/etc/app/conf.ini", section="myapp")
]
DEBUG = Value(default=False, cast=as_boolean, help="Toggle debugging mode.")
DATABASE_URL = Value(default="postgres://localhost:5432/mydb", help="Database connection.")
Later this object can be used to print settings
>>> config = AppConfig()
>>> print(config)
DEBUG=True - Toggle debugging mode.
DATABASE_URL='postgres://localhost:5432/mydb' - Database connection.
or with __repr__()
>>> config = AppConfig()
>>> config
AppConf(loaders=[Environment(keyfmt=EnvPrefix("MY_APP_"), EnvFile("main.env")])
extended
class TestConfig(AppConfig):
class Meta:
loaders = [IniFile("test_settings.ini"), EnvFile("main.env")]
overridden at runtime
>>> dev_config = AppConfig(loaders=[IniFile("dev_settings.ini")])
>>> dev_config.DEBUG
True
accessed as dict or object
>>> config.DEBUG
False
>>> config["DEBUG"]
False
iterated
>>> for setting in config:
... print(setting)
...
('DEBUG', Value(key="DEBUG", help="Toggle debugging on/off."))
('DATABASE_URL', Value(key="DATABASE_URL", help="Database connection."))
or passed around
def do_something(cfg):
if cfg.DEBUG: # this is evaluated lazily
return