| Project: | LEOGPS |
|---|---|
| Github: | https://github.com/sammmlow/LEOGPS |
| Documents: | https://leogps.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ |
| Version: | 1.3 (Latest) |
| Author: | Samuel Y. W. Low |
|---|
LEOGPS
LEOGPS is an open-source Python software which performs relative satellite navigation between two formation flying satellites, with the objective of high accuracy relative positioning. Specifically, LEOGPS solves for the double-differenced baseline (using float ambiguity resolution) between satellites flying in formation in Low Earth Orbit (LEO). As such, the relative positioning accuracy diminishes with increasing formation baseline lengths.
LEOGPS currently supports only observations from the GPS constellation (L1/L2 frequency), with observation files in RINEX v2.XX format. LEOGPS also uses the precise ephemeris (.EPH) and clock bias and drift files (.CLK) provided by the University of Bern, Center for Orbit Determination in Europe (CODE). As such, the coordinate frame used in the relative positioning is the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRS) which is an Earth-Centered Earth-Fixed (ECEF) frame. Since the ephemeris files and RINEX v2 observations default to GPS Time, it is very important to also note that the time scale used in LEOGPS output files is GPS Time (as opposed to UTC).
This project also gives sincere appreciation and credit to the University of Bern, for their provision of the CODE FTP.
Installation and First Steps
First, clone this repository by running in your terminal (or Git Bash):
git clone https://github.com/sammmlow/LEOGPS.git
Second, you should do a pip install in your terminal of Martin Valgur's Pythonic translation of Yuri Hatanaka's compression library for RINEX files
pip install hatanaka
The Hatanaka library in Python was kindly contributed by Martin Valgur in v1.1, and replaces the older "RNX2CRX" (and GZIP, thanks to the unlzw3 library) which are Windows-only executables, making the (de)compression possible across all platforms.
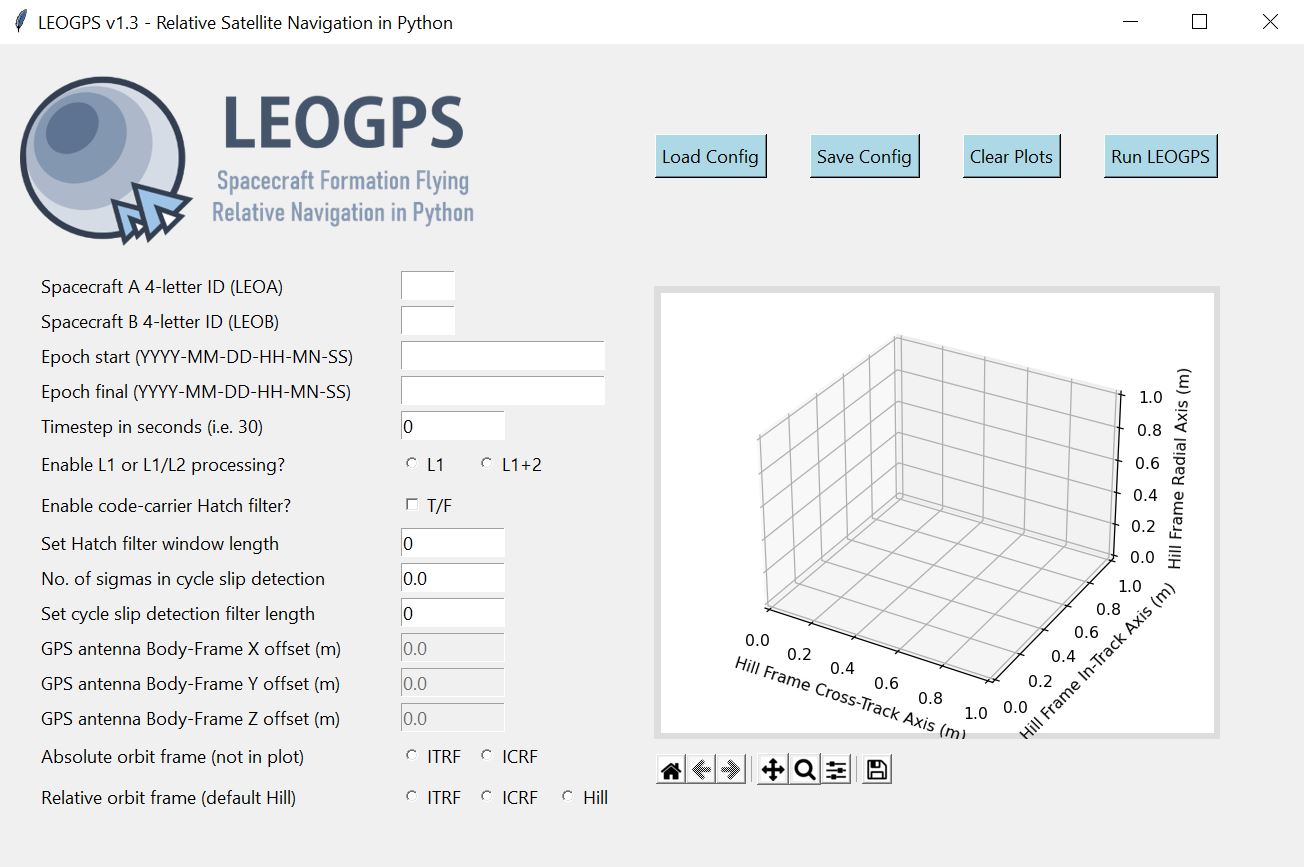
The user can then run the application by running 'leogps.py', in the main directory, and you should see the LEOGPS GUI launch:
Next, you can paste the two RINEX observation files of your LEO satellite pairs in the inputs folder, key in your configuration parameters, and hit the 'Run LEOGPS' button. That's it! LEOGPS will automatically source for the precise daily ephemeris and clock solutions, and process the raw GPS measurements to produce a report file in "LEOGPS_Results.txt" comprising:
- The single point positions and velocities of both LEOs.
- Precise baseline vectors between the two LEOs.
- Dilution of precision values.
LEOGPS will also output plots and reports on the interpolated GPS satellite ephemeris and clock biases.
For full documentation, please refer to the LEOGPS Read-The-Docs.
Other Package Dependencies
Recommended Python Version > 3.6
Core libraries necessary: NumPy (v1.14 and above), matplotlib, hatanaka
Standard Python libaries: os, copy, math, datetime, decimal, shutil, subprocess, warnings, urllib.request
Libraries for GUI: PIL, tkinter
Tested on Python version 3.6.5 (Anaconda with default packages).
Contact
If you have any queries feel free to reach out to me at:
Last Modified on 20-Sep-2021