Logistic Regression Advanced Case Study
Gender Classification: Predicting a person's gender based on their weight and height
1. Introduction
We turn our attention to classification. Classification tries to predict, which of a small set of classes, an observation belongs to. Mathematically, the aim is to find $y$, a label based on knowing a feature vector $x$. For instance, consider predicting gender from seeing a person's face, something we do fairly well as humans. To have a machine do this well, we would typically feed the machine a bunch of images of people which have been labelled "male" or "female" (the training set), and have it learn the gender of the person in the image from the labels and the features used to determine gender. Then, given a new photo, the trained algorithm returns us the gender of the person in the photo.
Logistic regression is a supervised learning classification algorithm used to predict the probability of a target variable. The nature of target or dependent variable is dichotomous, which means there would be only two possible classes. Mathematically, a logistic regression model predicts P(Y=1) as a function of X. It is one of the simplest ML algorithms that can be used for various classification problems such as spam detection, Diabetes prediction, cancer detection etc. Here , we use the Logistic regression model to predict the gender(Male/Female) of the person based on their weight and height . The data set contains three columns
- Height in inches
- Weight in pounds
- Gender (Male/Female) of the person
2. Visualization & Feature Engineering
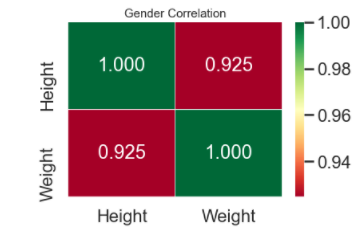
Let's explore the correlations and see which features separate the Male\Femals populations
From the visualizations avove, we could fairly say that their is a clear correlation between Weight and Height.
3. Model Tuning
The model has some hyperparameters we can tune for hopefully better performance. In order to tune the parameters of the model, a mix of cross-validation and grid search will be used. In Logistic Regression, the most important parameter to tune is the regularization parameter $C$. Note that the regularization parameter is not always part of the logistic regression model.
The regularization parameter $C$ is used to control for unlikely high regression coefficients, and in other cases can be used when data is sparse, as a method of feature selection.
Let's use 2 methods to perform model tuning and selecting the regularization parameter $C$:
- Writing our own loops to iterate over the model parameters
- Using GridSearchCV to find the best model
We use the following cv_score function to perform K-fold cross-validation and apply a scoring function to each test fold. In this incarnation we use accuracy score as the default scoring function.
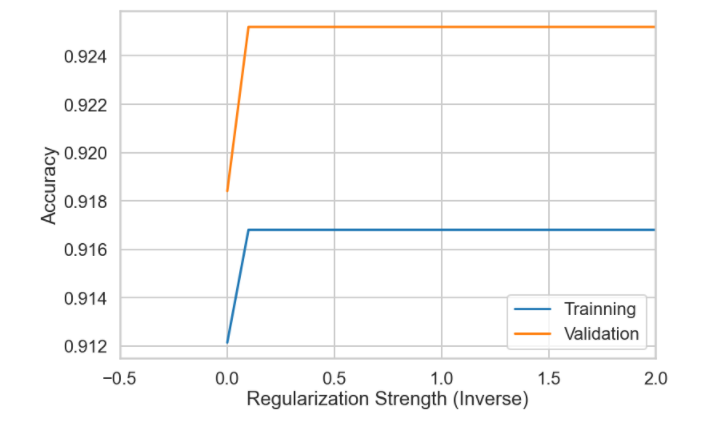
4. Training vs. Validation
After completing above steps we have conculded that the best regularization parameter C: 1 correspondes to the max validation score: 0.9172
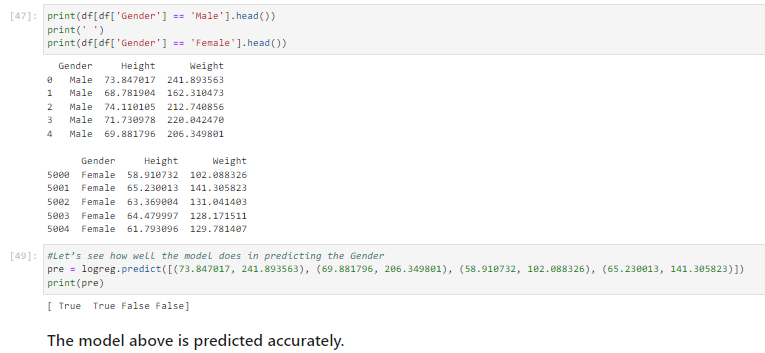
5. Model Performance
- Basic Logistic Regression (Unregularized): 0.9172
- Tuned Logistic Regression Parameters: {'C': 1}Best score is 0.9168
- Logistic Regression Accuracy Score (Regularized): 0.9252